Spotting AI-Generated Text
As AI writing tools become increasingly sophisticated in 2025, distinguishing between human and machine-written content has become both more challenging and more important. This comprehensive guide equips you with expert techniques to identify AI-generated text across educational, professional, and digital contexts.
Why Detection Matters
AI-written content has become increasingly prevalent in education, journalism, marketing, and other fields. Detecting it is crucial for several important reasons:
Academic Integrity
Educators need to prevent student plagiarism and ensure assignments reflect students’ actual learning and abilities rather than AI capabilities.
Content Authenticity
Publishers and media outlets must verify that content reflects genuine human expertise and perspective to maintain credibility.
Misinformation Prevention
As one guide notes, “without a human touch, misinformation spreads, and brands lose credibility.” AI detection helps combat fake content.
The rise of advanced language models like GPT-4 has made AI text detection both more challenging and more important. When AI content passes as human-written, it can have serious consequences:
- Undermines educational assessment integrity
- Erodes trust in published content
- Creates unfair advantages in competitive environments
- Facilitates the spread of synthetic misinformation at scale
- Reduces the value of genuine human perspective and creativity
Video: An investigation into whether current AI detection tools actually work
Key Linguistic and Stylistic Clues
AI-generated prose often carries subtle linguistic signatures that can help detect its origin. Here are the key patterns to watch for:
1. Generic, Buzzword-Filled Language
AI tends to overuse certain “safe” adjectives and businessy terms. Words like “essential,” “vital,” “boost,” “drive,” “ensure” and other stock phrases often appear repeatedly in AI text. Human authors usually use a more varied or domain-specific vocabulary. By contrast, AI text often feels generic or clichéd.
2. Repetitive Phrasing and Structure
AI models often repeat sentence patterns or connectors. For example, a paragraph might string together clauses like “By doing X, you can achieve Y, and also Z” multiple times. AI writing sometimes uses the same transition words or phrases in back-to-back sentences (“By focusing on…, By integrating…, By leveraging…”). Humans naturally vary sentence openings and phrasing more.
3. Overly Formal or Monotone Tone
AI prose is typically very polished and impersonal. It often maintains a neutral, evenly formal tone throughout, with little slang, humor or personal voice. Emotional cues, anecdotes or first-person perspective (“I” or “we” reflecting personal experience) are usually missing. As one analysis notes, AI writing “may lack emotion or personality, resulting in a robotic or flat tone”. If the text sounds unusually detached or diplomatic, suspect AI origin.
4. Flawless Grammar and Uniform Style
AI rarely makes simple typos or obvious errors. A piece of writing that has zero spelling/grammar mistakes – especially on a long or technical topic – can actually be a red flag. Human writers inevitably have quirks or occasional slips (for example, a typo or unusual phrasing). If the writing is mechanically perfect in every sentence (all syntax correct, all punctuation uniform), it might be auto-generated.
5. Low Variation (Predictability) – Perplexity and Burstiness
In human writing, sentence lengths and word choices vary a lot; in AI text they tend to be more uniform. AI systems aim for the most probable next word, so their output often has low perplexity (very predictable phrasing) and low burstiness (sentences all similar lengths).

Visual representation of perplexity and burstiness differences between AI and human writing
In contrast, humans often mix short, punchy sentences with longer, complex ones. For example, a human writer might compose a poetic, high-perplexity line like “Every second on the clock erupted into a cascade of paradoxical moments…”, whereas an AI might produce a straightforward line like “The clock ticked steadily, marking the seconds.” Uniform, “boring” sentence structure (all medium-length, similarly constructed sentences) suggests AI.
6. Vague Generalizations, Lack of Deep Insight
AI text often stays at a surface level. It tends to make broad statements without specific examples or original analysis. For instance, an AI might say “lifelong learning is important because it opens new opportunities” in very general terms, whereas a human writer might use a concrete metaphor or story. If the writing uses lots of disclaimers and clichés (for example “Studies show… Experts agree…”) but gives no detailed data or personal perspective, it may be AI-generated.
7. Awkward or Unusual Language
Look for odd word choices or phrasing that a human probably wouldn’t use. AI sometimes spits out stilted or over-formal language (“in order to”, “moreover”, “furthermore”) in places where a person would use a simpler word or break a sentence differently. It may repeat similar sounding words too closely or misuse idioms. In general, a bit of “unusual language” – too-literary phrases or slightly off grammar – can paradoxically signal AI, since it’s trying too hard to sound polished.
8. Excess of Structure or Formatting
Some AI generators favor lists and bullet points to organize information. An unusually structured document (lots of bullet lists or numbered steps with no narrative text) might be a clue. Likewise, overly organized paragraphs with very obvious topic sentences might hint at algorithmic generation.
Contextual and Metadata Clues
Beyond the writing itself, examining the context provides valuable clues about AI-generated content:
Unnatural Publication Patterns
A burst of content coming at odd hours or all at once may indicate automation. For instance, a news outlet suddenly churning out dozens of articles in minutes could suggest AI writing. Likewise, if a social media account posts long articles late at night or at perfectly regular intervals (24 hours apart, etc.), be suspicious.
Implausible or Missing Attribution
Check the author and metadata. For example, if an article claims to be written by someone who wasn’t even born at that time, or from a location that doesn’t exist, it’s likely fabricated. AI tools might leave blank author fields or insert obvious placeholders.
Questionable Sources and Facts
AI often hallucinates sources. If the text cites studies or quotes with no evidence, verify them. Many AI models generate convincing-looking book or journal citations that are entirely made up. A practical tip: pick a random reference or quote and search it. If the exact source cannot be found, the text was likely generated by AI.
Outdated or Inaccurate References
Some AIs have a cutoff date for training data. Check whether the content correctly references recent events or news. If the text misdates something or generalizes about recent happenings, it might be AI. For example, a summer-2025 essay that only discusses events up to 2021 without explanation could be suspect.
Sudden Style or Topic Shifts
Within a single document, a big change in tone, style or complexity can be telling. For example, the first half of an essay might read smoothly and informally, then abruptly switch to a very formal tone. This may indicate that part was AI-generated and part human (or two different AIs).
Digital Fingerprints
In collaborative documents or websites, check revision histories. AI-generated content is often pasted in all at once, whereas human writing typically evolves through multiple edits and revisions over time.
Video: Practical advice for educators on detecting AI-generated homework submissions
Practical Tips and Tools for Verification
No single test is foolproof. The best approach is to combine multiple clues and use tools intelligently:
AI Detection Software (with Caution)
A number of online tools claim to flag AI-written text. These tools analyze statistical patterns like perplexity and burstiness. For example, GPTZero explicitly checks sentence diversity and word unpredictability. These can be a useful first pass, but don’t rely on them alone.
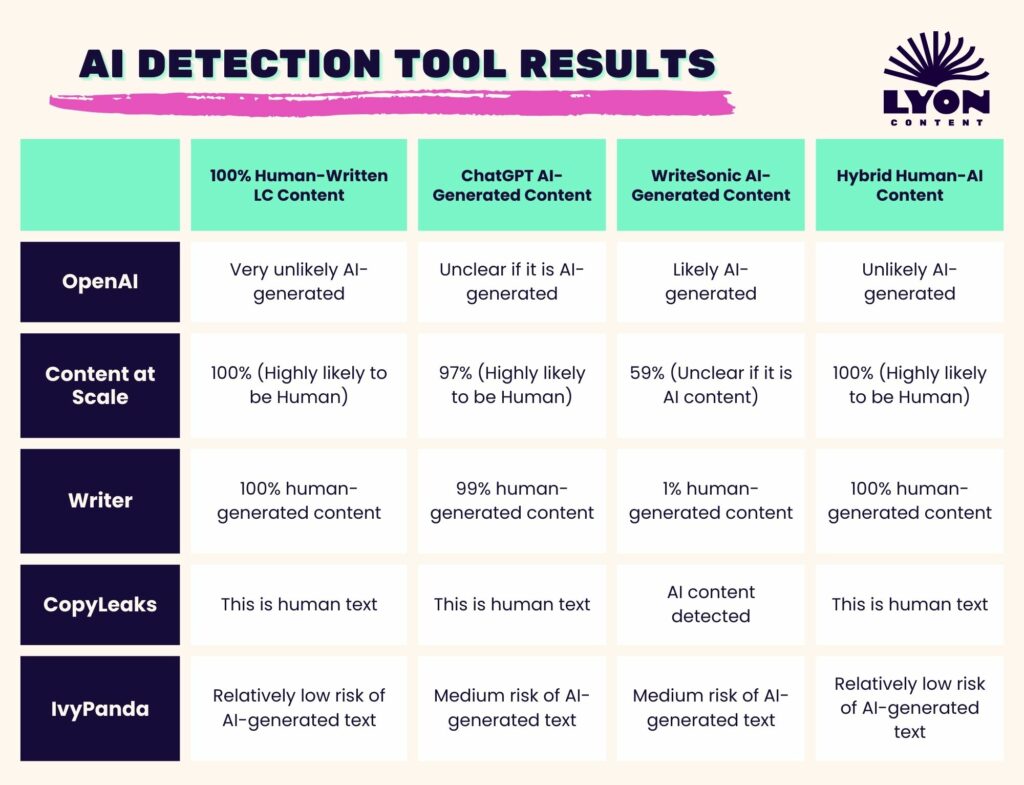
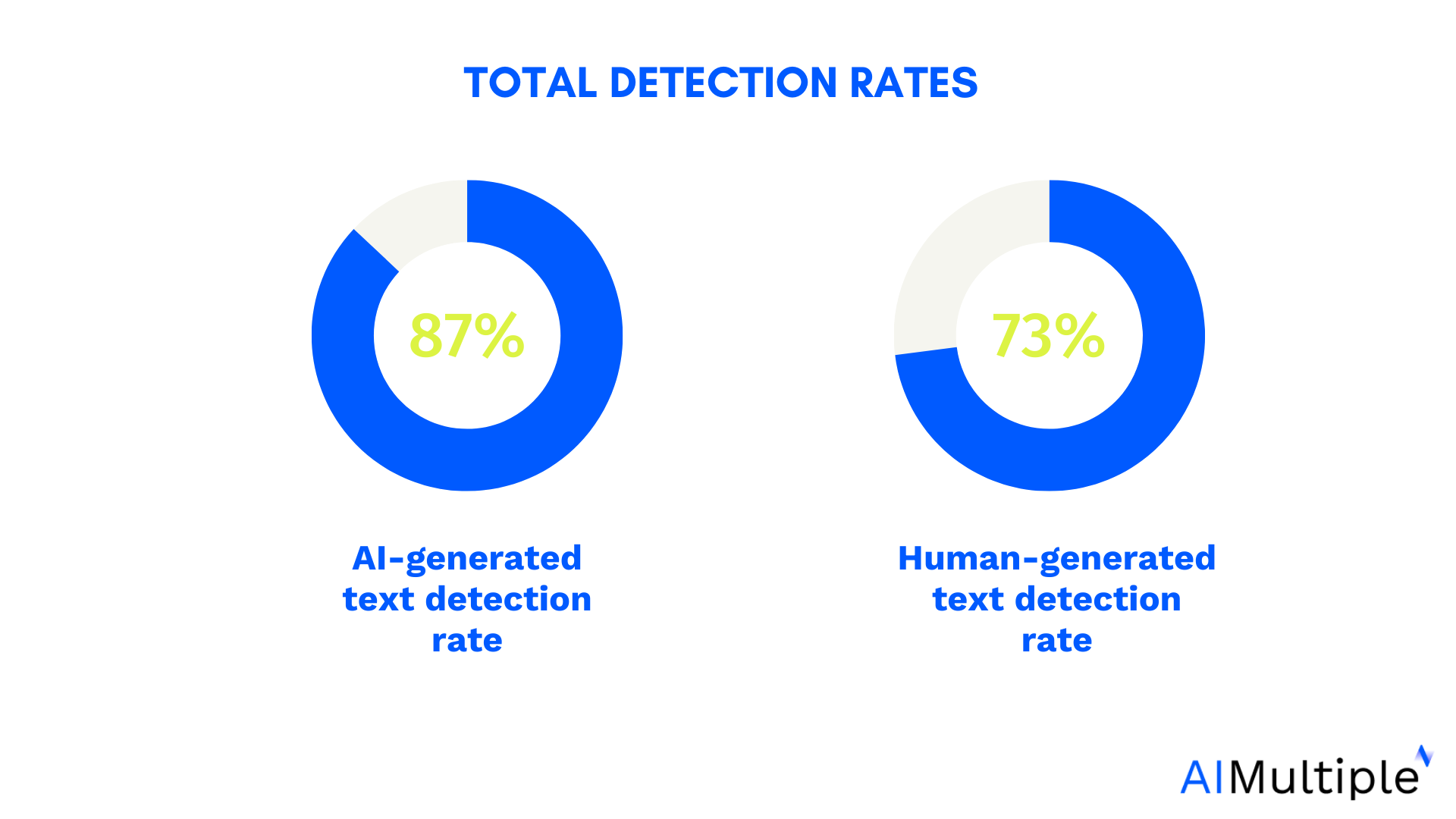
Comparison of popular AI detection tools and their accuracy rates
Studies show detection tools are only ~80% accurate and often yield false positives on unusual but human text. Indeed, well-edited AI content or cleverly paraphrased text can fool many detectors. Use any “AI score” as just one data point, not definitive proof.
Popular AI Detection Tools in 2025:
- GPTZero – Focuses on perplexity and burstiness metrics
- Originality.AI – Uses advanced machine learning for detection
- Turnitin’s AI Check – Popular in educational settings
- Copyleaks – Combines plagiarism and AI detection
- Scribbr – Free option with tiered features
Compare to Known Writing
If possible, see if the suspicious text matches writing samples by the purported author. Educators should compare a student’s submission to that student’s previous essays or notes. Look for big deviations in vocabulary, style, or error patterns. If a normally casual writer suddenly produces extremely formal prose, that’s suspicious.
Fact-Check Content
Manually verify any facts, statistics or quotations. AI models can invent data, dates or studies that sound plausible. If a text cites a study or figure, search for it. False specifics (“According to a 2024 study by the Institute of Y”) can betray AI generation. Also, put suspicious sentences into Google or academic databases: if you find no matching source, it was likely made up.
Ask Questions or Seek Revision Histories
In a scholastic or workplace setting, quiz the author about their content or request drafts. If a student can’t explain their own paper’s key points, it may indicate they didn’t write it. In collaborative docs (like Google Docs), review the version history. AI-generated text is often pasted in all at once, whereas genuine writing evolves over time.
Use Plagiarism and Reverse-Search Tools
Sometimes AI text is copied from common sources or from previous AI outputs. Run the suspicious text through plagiarism checkers. If the text—or significant parts of it—appear elsewhere on the web (in books, papers, or known AI datasets), that’s a clue.
The ChatGPT Self-Identification Trick
One clever technique shared by educators: copy the suspicious text and ask ChatGPT directly “Did you write this?” Surprisingly, the AI often honestly admits when text was generated by itself or similar models. While this won’t work forever as models evolve, it’s currently an effective method for quick verification.

Comparison of detection approaches between different AI detection tools
Important Reminder:
Rely on multiple signals. A single telltale word or technical limitation isn’t enough. But when many red flags align (e.g., very generic language, no typos, no verifiable sources, and an abnormal publication pattern), the case for AI is strong.
Examples: Human vs. AI-Generated Text
Comparing examples side-by-side illustrates the subtle differences between human and AI writing:
| Human-Written Excerpt | AI-Generated Excerpt |
|---|---|
| “Life can be seen as an unending journey, like the sun that arches daily from dawn to dusk. This constant movement represents lifelong learning, a ceaseless quest for growth and understanding.” | “In the grand tapestry of human existence, lifelong learning is a pillar of enlightenment and a pathway to a meaningful and good life.” |
| “Every second on the clock erupted into a cascade of paradoxical moments, each a universe unto itself. The teapot sang an opera of hot, swirling tea, every steamy note a symphony of flavor.” | “The clock ticked steadily, marking the seconds. I poured hot water into the teapot, and a soothing aroma filled the room.” |
| “I crashed my mom’s car when I was 17—backing into a telephone pole while trying to parallel park, of all things—and I still remember the hollow feeling in my gut when I had to call her from work.” | “Many teenagers experience their first automobile accident during the learning phase of driving. This often involves minor collisions during challenging maneuvers such as parallel parking, which can result in significant emotional distress.” |
Notice how the human examples (left) show more creativity, varied sentence structure, specific personal details, and unexpected language. The AI text (right) is grammatically correct but more formulaic, general, and consistent in structure.
Key Differences in The Examples:
Human Writing:
- Uses vivid, unexpected metaphors (sun arching, teapot singing)
- Varies sentence length dramatically (very short to complex)
- Includes specific personal details (age 17, calling mom from work)
- Contains more creative, unpredictable language
- Shows emotional vulnerability and specific sensory details
AI Writing:
- Relies on general, abstract concepts (“grand tapestry,” “pillar of enlightenment”)
- Maintains even, medium-length sentences throughout
- Uses formal, academic tone consistently
- Presents general observations rather than specific experiences
- Employs predictable, common phrasing (“marking the seconds,” “emotional distress”)
Future of AI Text Detection
As AI writing technology continues to evolve, detection methods must adapt. Here are some emerging trends:
Watermarking
Some AI developers are implementing invisible watermarks in their generated text. While promising for transparency, these can often be removed by simple rephrasing or using different AI models.
Multi-modal Detection
Future detection may analyze multiple factors beyond just the text itself—including creation patterns, metadata, context, and cross-referencing with known AI-generated content repositories.
Human-in-the-loop
The most effective approaches will likely combine automated detection tools with human expertise and judgment—especially for high-stakes contexts like academic assessment.
Focus on Process
In educational contexts, emphasizing process documentation (drafts, outlines, research notes) rather than just final products may become more important for verifying original work.
“The cat-and-mouse game between AI content generation and detection will continue. The most sustainable approach isn’t just better detection, but creating contexts where transparency about AI assistance becomes the norm rather than something to hide.”
Conclusion
Spotting AI-generated text requires a multi-faceted approach. No single method is foolproof, but by understanding the linguistic patterns, contextual clues, and using appropriate detection tools, you can make informed judgments about content origin.
As AI technology continues to advance, the distinction between human and AI writing will become increasingly nuanced. The most effective strategy combines technical tools with human judgment and critical thinking. Whether you’re an educator, publisher, or content consumer, developing these detection skills is essential for maintaining authenticity and trust in our increasingly AI-augmented information landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- Look for patterns of generic language, repetitive structure, and uniform tone
- Be alert to suspiciously error-free text with consistently medium-length sentences
- Pay attention to contextual red flags like questionable sources and sudden style shifts
- Use detection tools as one data point, not definitive proof
- Compare with the author’s known writing style when possible
- Verify facts, sources, and citations that seem too perfect or convenient
- Remember that AI detection is probabilistic—rely on multiple signals



